Managing employee benefits and contributions is a critical responsibility for employers in India, and the Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) facilitates this process. However, there are times when the ESIC payment link provided by the corporation may not function correctly, causing delays and complications. Fortunately, there is an alternative solution available through the ESIC portal, utilizing the double verification of the challan module. In this blog article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to the alternative ESIC payment process, ensuring you can manage payments efficiently even if the primary link fails.
The Importance of an Alternative Payment Method
Payment issues can arise due to various reasons such as technical glitches, server downtime, or connectivity problems. These issues can lead to significant delays and stress, especially when it comes to meeting statutory deadlines. The alternative method of payment via the ESIC portal ensures that employers can still fulfill their obligations without any hindrance. This alternative method leverages the double verification of the challan module, a robust feature of the ESIC portal.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide to Alternative ESIC Payment
- Login to the ESIC Portal:
- Begin by opening your web browser and navigating to the official ESIC portal (www.esic.gov.in).
- Enter your User ID and Password to log into your ESIC account securely.
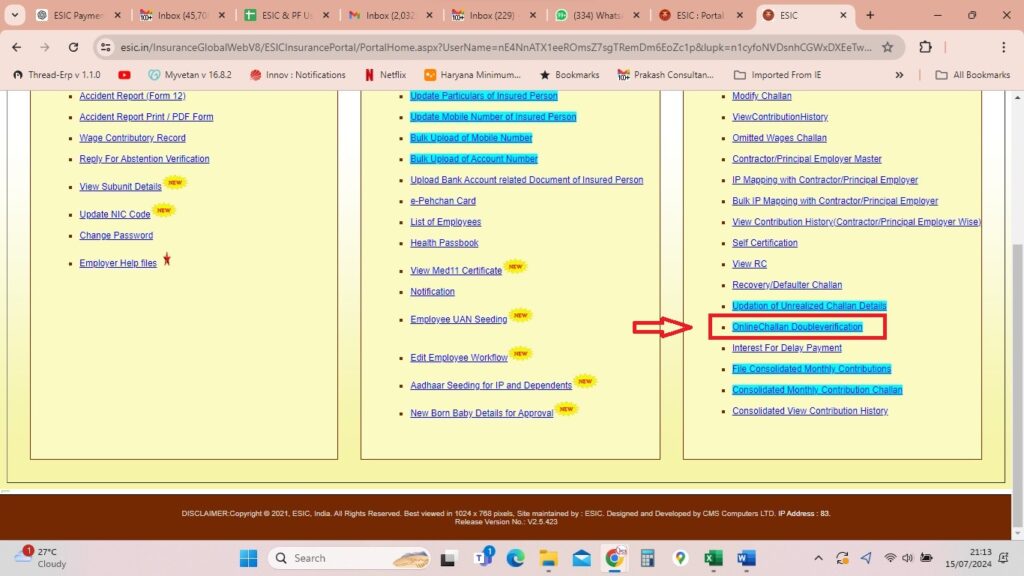
- Access the Challan Module:
- Once logged in, locate the ‘Challan’ module on the dashboard or in the menu options. The layout may vary slightly depending on updates to the portal, but the module is typically easy to find.
- Click on the ‘Challan’ module to proceed to the next section where you can manage and verify challans.
- Utilize Double Verification:
- In the Challan module, you will find an option labeled ‘Double Verification’. This feature is designed to verify the details of the challan before proceeding with the payment.
- Click on ‘Double Verification’ to open the verification interface.
- Enter the Challan Number:
- The interface will prompt you to input the Challan number associated with the payment. The Challan number is a unique identifier for your payment and is crucial for verification.
- Carefully enter the correct Challan number and double-check for accuracy to avoid any errors that could complicate the payment process.
- Initiate Payment:
- After entering the Challan number, the system will display the option to make a payment. This ensures that you have verified the challan details before proceeding.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to move forward with the payment process. The portal will guide you through each step.
- Choose Your Payment Method:
- The ESIC portal offers multiple payment methods, including Net Banking, Debit Card, and Credit Card. Choose the method that is most convenient and secure for you.
- Complete the payment process by following the prompts provided by the portal. Ensure you are using a secure internet connection to protect your financial information.
- Confirmation of Payment:
- Once the payment is successful, the system will display a confirmation message. This confirmation serves as proof of payment and includes important details such as the transaction ID and amount paid.
- Save or print the confirmation for your records. It is essential to keep a copy of this confirmation for future reference and compliance purposes.
Advantages of Using the Double Verification Module
- Reliability: The alternative payment method via double verification is reliable, ensuring that payments can be made even if the primary link is down.
- Security: Payments made through the ESIC portal are secure and protected against fraudulent activities. The double verification process adds an extra layer of security.
- Convenience: Employers can manage and track their payments directly from the ESIC portal, making the process more streamlined and efficient. The ability to handle everything from one interface reduces the need for multiple systems and processes.
Tips for a Smooth Payment Process
- Double-Check Details: Always double-check the Challan number and payment details before proceeding. Errors in these details can lead to delays or incorrect payments.
- Use Secure Networks: Ensure you are using a secure internet connection to avoid any security breaches. Public Wi-Fi networks are not recommended for financial transactions.
- Keep Records: Maintain a record of all payment confirmations and transactions for future reference and compliance purposes. Proper documentation can help resolve any disputes or issues that arise later.
Conclusion
In the event that the ESIC payment link is not functioning, the alternative method of using the double verification of the challan module on the ESIC portal provides a seamless solution. By following the steps outlined above, employers can ensure that their ESIC payments are completed without any disruptions, maintaining compliance with statutory requirements and ensuring the well-being of their employees. Stay proactive and prepared by familiarizing yourself with this alternative payment method to handle any potential payment issues efficiently.
This detailed guide aims to empower employers with the knowledge to navigate the ESIC payment process smoothly, ensuring that their obligations are met promptly and securely.